Something strange about your observation?
All images taken of space can have certain quirks. Here is some information on the most common things you can find:
- Why are my images dark?
One of the first things you may have noticed when you loaded your image(s) into a FITS reading/processing software is that, to start with, the images are very dark and not much detail can be seen.
This is because the software is designed to count the number of photons hitting the detector, not to create pretty pictures on their own!
All we need to do in this case is to change the scaling of the image(s) in the Display menu using the sliders. This should reveal some more detail.
Image CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedUsing the Display and Scaling tools in the software to brighten a dark image (left) to get a detailed bright image (right) of Messier 27 If you are making a 3-colour image, we can only do this in LTImage; first, add the images into a 3-colour image and then separately change the Pixel value range for each colour/filter.
You will find that reducing the maximum pixel value (often by quite a lot) will bring out more detail and brighten your image.
Image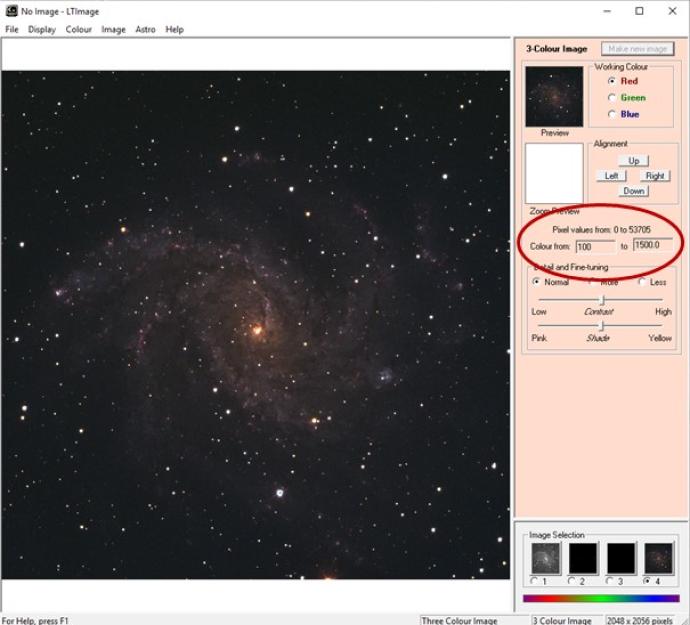 CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedUsing pixel value scales in the 3-colour image window to change the brightness of objects in the image (Note: in this case the pixel values have to be changed for all seperate colours to combine them!) - Why are my images blurry/grainy?
There are a few things that we have to take into account here, some under our control and some that are not:
The Moon
Much like how we cannot see stars during the day due to the brightness of the Sun, we get a similar effect from the Moon. The Moon gets brighter as it reaches the Full Moon phase. It reflects light from the Sun onto our atmosphere, which makes the night sky brighter. This is great for getting some nice Moon shots but makes faint objects very hard to see.
With deep sky or faint objects, changing the exposure time will make no notable difference. This is because the camera will still collect the scattered photons coming from the Moon. So, the best time to observe such objects is when the Moon is a New Moon. During this phase, it is not reflecting as much of the Sun’s light down onto our atmosphere. This is when the sky is at its darkest.
There is an option in our Go Observing section where you can choose to observe when the Moon is ‘Up’ or ‘Down’. This will maximise your chance of getting a high-quality image.
Seeing
In astronomy, seeing is the name given to the effect that makes stars ‘twinkle’. Stars do not actually ‘twinkle’ at all. The photons from these objects have travelled for years in a straight path but get ‘knocked around’ as soon as they reach our atmosphere. The twinkle that you see is the photons hitting and/or being scattered by particles in the atmosphere.
Image CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedTwo observations of NGC 1788 (the Foxface nebula) on different nights. We can see that the image on the right (good seeing) is clearer and has more detail. In the image on the left (bad seeing), the stars and clouds are blurred and fuzzy. Seeing is mainly caused by turbulence in the atmosphere. How high the observing site is makes a difference. The higher you are, the less atmosphere for the photons to travel through. Engineering can correct for different levels of seeing on the night of observation due to turbulence, but it still poses challenges.
If your image is slightly blurry, it is likely that the seeing on the night of the observation was not good and the photons were scattered more intensely. The best quality images come when the atmosphere above the observing sight is at its calmest. As a calm atmosphere cannot be planned, if you are not happy with your image, you will have to submit a new observation request.
Seeing also has different effects on different filters (because they observe at different wavelengths). When using RVB filters for your 3-colour observations, the B filter (closer to the ultraviolet side of the electromagnetic spectrum) suffers more from the conditions of our atmosphere, so it will sometimes look grainier than either R or V filters.
- Why are my images brighter than other observations of the same object?
The answer to this is usually exposure time.
The camera collects photons from the entire field of view, not only the object being observed. Longer exposure times (30-120 seconds) will make the whole image brighter.
- Why do the stars in my images look strange?/Why do they have splodges in the middle?
You may have an observation with stars or bright regions that have blocky/smudged centres of colour that ‘bleed’ out onto the image. This is called saturation.
Image CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedAn example of a saturated star. The right image is a zoom in of the star. The black patch in the centre is clearly visible along with diffraction spikes coming out from the star. It is most common when trying to observe a faint object, like a nebula, when there are also bright stars in the field of view. When observing with a high exposure time (for example, 120 seconds), the detector collects more photons from the dim areas of an object and, thus, more detail.
But some stars in the field of view can be much brighter than anything around them and the detector will also collect photons from these stars for 120 seconds. This saturates the pixels on the camera; there are simply too many photons for the detector cell to hold and the charge bleeds into the surrounding cells.
The best way to observe an object like this (a faint object but with bright regions/objects in the shot) is to take many low-exposure observations and then stack them together. This will make objects such as stars brighter, but it will not saturate them.
- Why don't my images include the entire object?
You may notice that when observing an object, such as the Rosette Nebula or the Fishhead Nebula, you cannot see the whole thing. This is because some objects are so big in that the entire object cannot fit into a single frame of the camera.
Most instruments on telescopes cannot zoom in and out of objects. Instead, they have a set field of view on the night sky!
- Why does my image have a bright line going straight through it?
You may have found an image that looks like this whilst using telescope observations. As we can see, there is a bright straight line cutting across the image in the bottom-left.
Image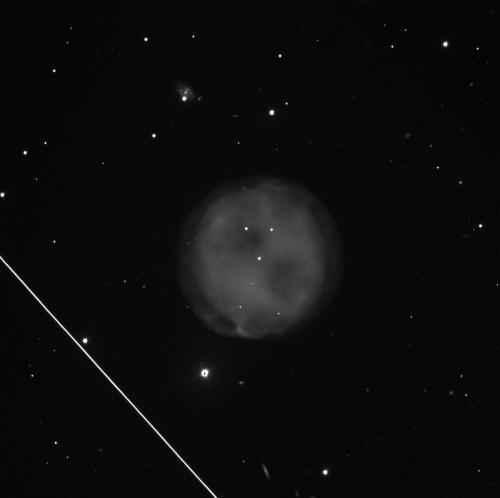 CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedThis is in fact a satellite! Sometimes, satellites just happen to cut across the telescope's field of view while it is observing a target. Sadly, there is no option to remove the line from the image, only to request another observation!
You may be wondering why the line is so bright compared to the stars in the image. This is because the satellite is so much closer than the objects we observe (a few thousand kilometres rather than light-years away).
We capture the small amount of light that the satellites reflect from the Sun, Moon or light diffracted by Earth's atmosphere that hits it. This means the images can collect a lot of the light bouncing off!
- Why does my image have a dark line going straight through it?
Sometimes on your observation, a vertical dark line may appear.
Image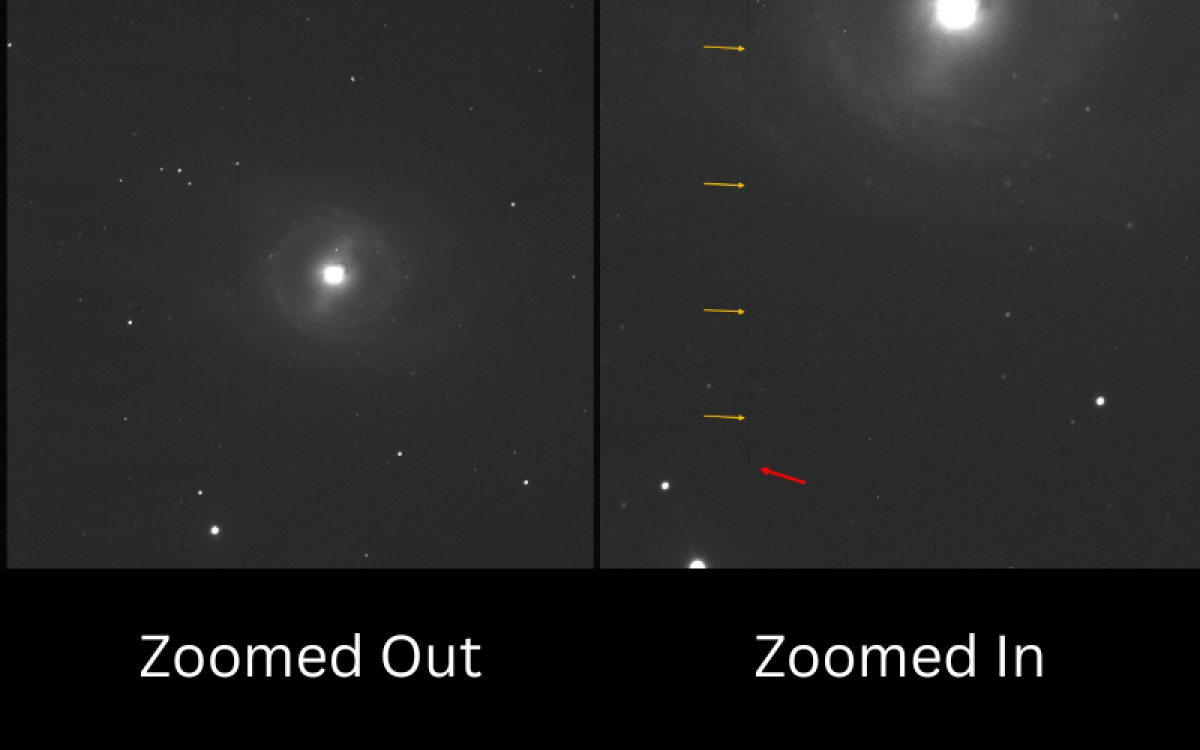 CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedImage of a galaxy with a line of dead pixels (yellow arrows point out the column of dead pixels, and the red arrow points to the dead pixel which makes the above pixel information void) These are called dead pixels. They are specific to how a CCD camera (the camera used on the back of a telescope) works and how they read out data. The lines can vary in length depending on how far up the CCD the bad pixel lies.
As a CCD reads out in vertical lines, a 'dead' pixel when read out will make the data void for the rest of the column. This is why the line then carries up to the top of the image.
- Why does my image have small lines or dots scattered across it?
Sometimes, you may find small lines (usually a couple of pixels) scattered across your image. If you have a coloured image, these will appear as coloured pixels/lines.
The white version (on a single-colour image) will look something like this:
Image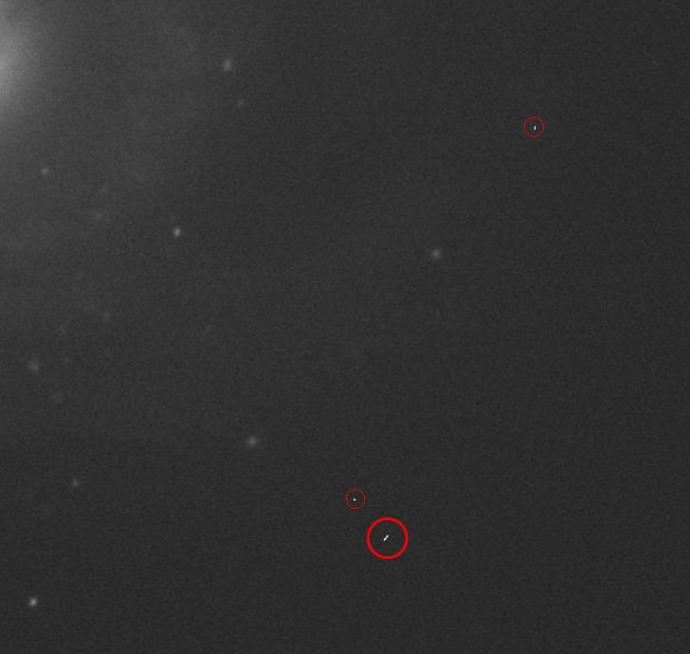 CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedZoomed in section of an image with cosmic rays (circled in red) that appear as random white pixels The reason for this is that tiny particles called cosmic rays are constantly finding their way through the atmosphere and hitting the telescope detector. Cosmic rays can come from inside our Solar System or from outside. The lower-energy ones come from the Sun and the high-energy ones from events outside the Solar System (like supernova explosions). The particles travel close to the speed of light.
Stopping cosmic rays from hitting the detector is impossible, but there are processes which can be done to the image to even it out. The Schools' Observatory usually does this before you get the image back, but some can slip through the net!
